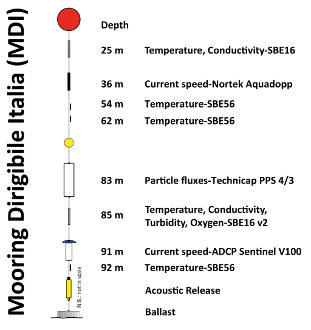
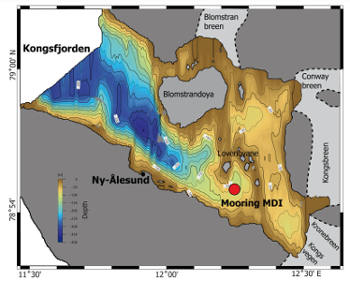
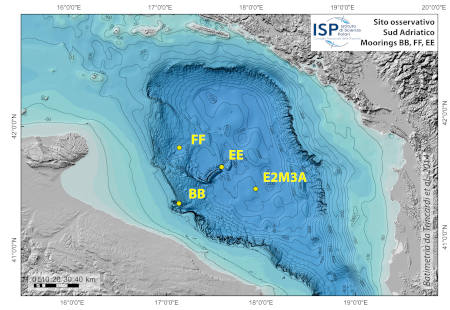
High Performance Liquid Chromatograph Agilent 1100 Series HPLC Systems
Brief description
The HPLC-MS/MS system allows to quantitatively determine polar organic compounds in several environmental and vegetable matrices and biota samples. It is commonly used to investigate specific markers of sources or environmental processes in samples collected in polar regions. It is used to determine levoglucosan, key tracer of biomass burning, in ice core samples to provide historical profiles of fire regimes in paleoclimatic studies. Several water soluble organic compounds (free and combined amino acids, phenolic compounds) are determined using HPLC-MS/MS in aerosol samples to define chemical composition of atmosphere in urban and polar samples. Polar pesticide or toxins are commonly determined with HPLC-MS/MS in fresh water, sea water, biota or vegetable samples.
Instrument
High Performance Liquid Chromatograph Agilent 1100 Series HPLC Systems (Waldbronn, Germany) with a binary pump, vacuum degasser, autosampler and thermostated column compartment coupled with an API 4000 Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (Applied Biosystem/MSD SCIEX, Concord, Ontario, Canada) using a TurboV source.
Contact person: Dr. Roberta Zangrando - roberta.zangrando AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Analysis of discrete samples of several matrices: ice, snow, atmospheric aerosol, lacustrine water, fresh water, sea water, sediment, vegetable and biota samples. Analysis of polar organic compounds such as for example anhydrosugars, amino acids, phenolic compounds, organic acids.
Agilent 1100 series HPLC system coupled with API 4000, High Performance Liquid Chromatograph coupled with tandem mass spectrometer (HPLC-MS/MS). (IMAGE)

Liquid chromatograph UHPLC mod. Dionex Ultimate 3000 Dual Pump RS
Brief description
This instrument is the key system to perform semicontinuous analysis of organic compounds in ice core samples.
Instrument
Liquid chromatograph UHPLC mod. Dionex Ultimate 3000 Dual Pump RS (Thermo ScientificTM) with vacuum degasser, column thermostat.
Contact person: Dr. Elena Barbaro - elena.barbaro AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Semicontinuos analysis of ice cores. This system is coupled with continuous flow analysis (CFA).
Dionex Ultimate 3000 Dual Pump RS Thermo Scientific, Liquid chromatograph UHPLC Dual Pump (IMAGE)

Mercur Plus - Analytik Jena AG, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS).
Brief description
Cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS) is an analytical technique used for the quantification of mercury at trace/ultra-trace levels. This technique is mainly used on “clean” aqueous matrices (eg ice, snow, and water) from remote and uncontaminated areas.
The sensitivity of the instrument is fully harnessed by using official methods such as USEPA1631 version E or UNI-EN 15853: 2010. The Hg present in the matrix is oxidized to Hg2+ with BrCl solution and then reduced to elemental mercury(Hg0) con SnCl2. The Hg0 is stripped from the aqueous matrix using an inert carrier gas (argon) and successively transported to gold traps for the pre-concentration by amalgam formation. Following thermal desorption at T between 450-500 °C, the Hg0 is desorbed from the gold traps and is transported into a quartz cell.
Light from a mercury vapor lamp passes through the quartz cell that contains the sample mercury in a flow of argon carrier gas and excites all the mercury atoms which then emit a characteristic fluorescence radiation at 253.7 nm. The amount of light emitted by the mercury atoms in the sample is proportional to the amount of mercury passing through the quartz cell. The CV-AFS of the CNR-ISP is located inside a dedicated clean room.
Instrument
Mercur Plus - Analytik Jena AG, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS).
Contact person: Dr. Massimiliano Vardè - massimiliano.varde AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Aqueous matrices: atmospheric deposition, snow, ice, drinking water, mineral water, natural water, seawater. Mercury, as total mercury, or as dissolved, filtered and unfiltered after sample pre-treatment.
Mercur Plus - Analytik Jena AG, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS). (IMAGE)

Gas chromatograph coupled with mass spectrometer (GC-MS)
Brief description
The GC-MS system allows the quantification of volatile apolar compounds in environmental matrices. In the environmental field GC-MS finds main application in the determination of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) such as PCBs, PBDEs, PAHs, pesticides, in environmental matrices both in urban and remote areas such as polar areas. As well as it used in the determination of personal care products such as fragrances that have been observed not only in urban areas but also in Antarctica.
In the ISP-CNR there are 3 GC-MS systems. Among these, the system equipped with a cryogenic trap allows the preconcentration of volatile compounds (allowing the quantification of volatile compounds difficult to analyze in GC even at very low levels). There is also a GC-MS system equipped with a pyrolyser that allows the analysis of non-volatile materials such as plastic materials.
Instrument
• GC-MS 7890A-5975C (Agilent) /
• GC-MS GC7890A+MS5975C (Agilent) with cryogenic trap (MARKES Int)
• GC-MS GC6890+MS5973 (Agilent) with Pyrolysis system Pyroprobe 5000 Series
Contact person: Dr. Elena Argiriadis - elena.argiriadis AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Analysis of discrete samples of several matrices: ice, snow, atmospheric aerosol, lacustrine water, fresh water, sea water, sediment, vegetable and biota samples. Compounds analyzed: Apolar volatile compounds such as PCBs, PBDEs, PAHs, pesticids, fragrances, sterols.
GC-MS 7890A-5975C Agilent (IMAGE)





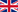
 Brief description
Brief description