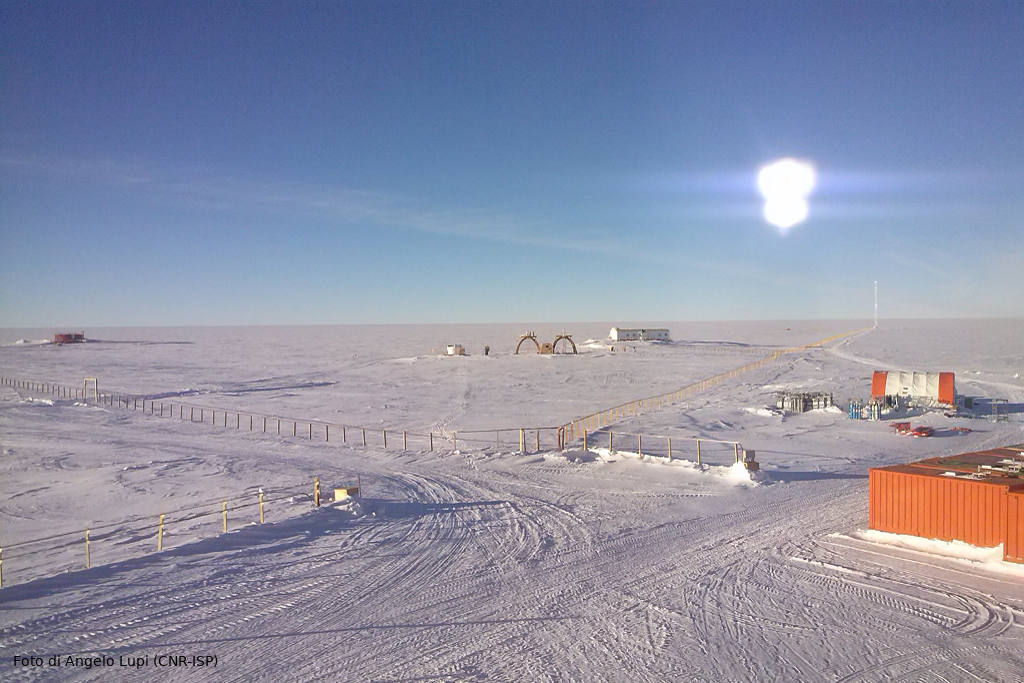
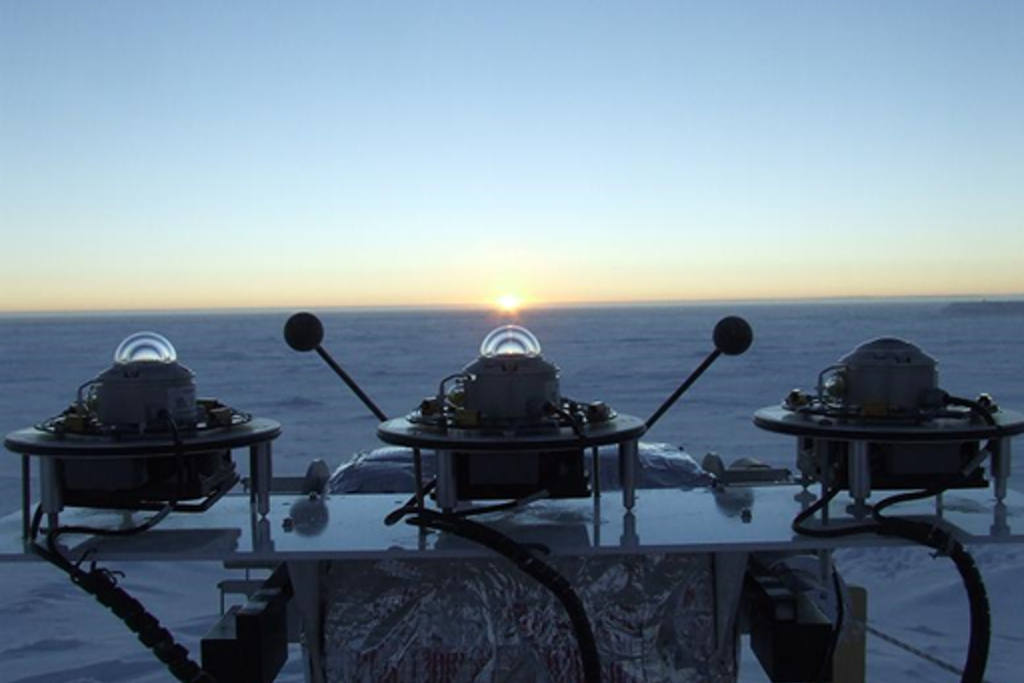
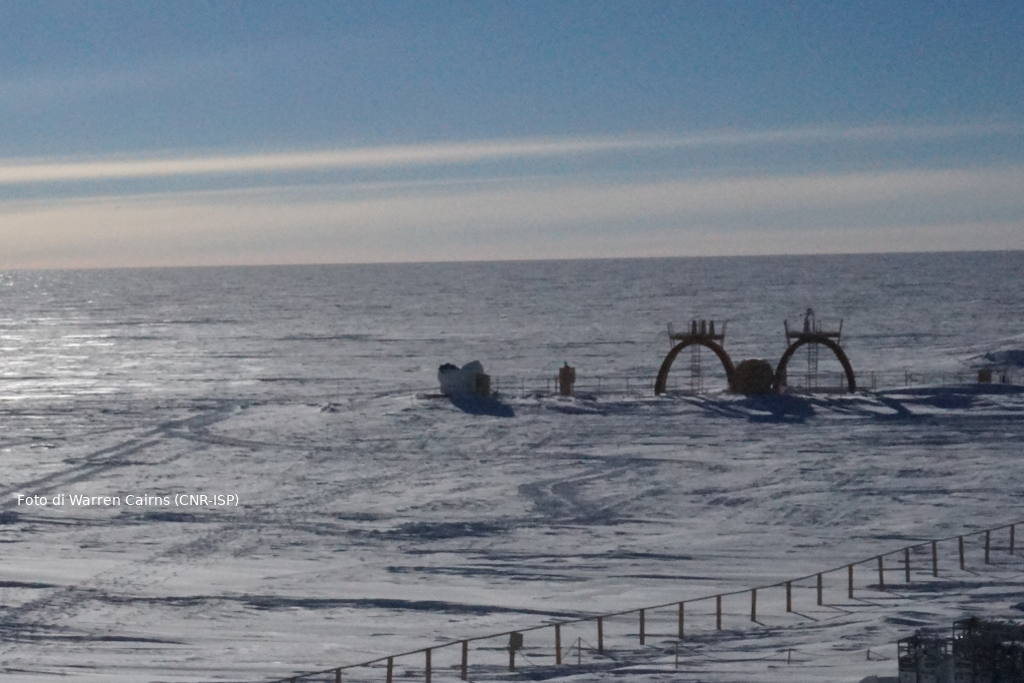
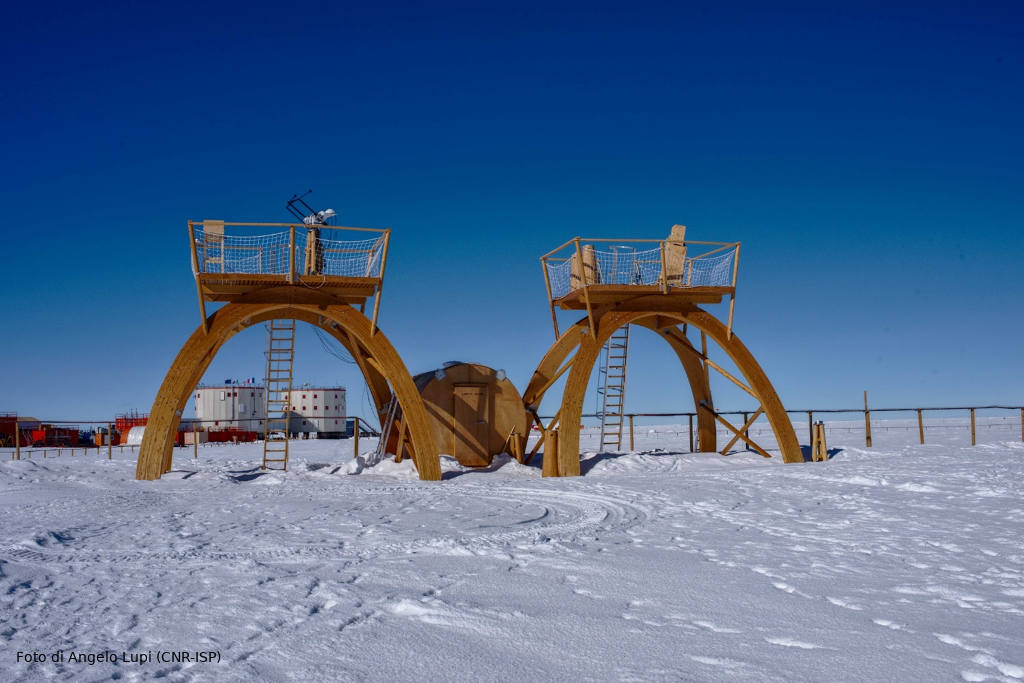
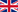
The BSRN was created to improve the quality of measurements of the Earth-atmosphere radiative fluxes that determine the thermal conditions and circulation of the atmosphere and the ocean. The ISP manages this observatory at the Italian-French Concordia station in Antarctica. Installed in 2006, the BSRN was funded by the PNRA and consists of a series of passive instruments (radiometers and photometers) that measure different components of the radiation balance (both in the solar and infrared spectrum), including the surface albedo.
In addition to these measurements, during the austral summer, the columnar content of aerosols is also measured by means of an SP02sun photometer, and the ultraviolet radiation spectrum by a UV-RAD radiometer, from which it is possible to obtain the ozone concentration, along the entire atmospheric column. Other measurements that are carried out as part of the observatory's activities are in collaboration with the Finnish Meteorological Institute (FMI) and concern the physical and optical properties of atmospheric particulate matter at ground level: its diffusion, absorption coefficients and dimensional distribution.
BSRN
Published in
Observatories
 Ministero dell'Universita e Ricerca
Ministero dell'Universita e Ricerca
Programma Ricerche Artico
Programma Nazionale di Ricerca in Antartide
 Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale
Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale
L'Italia e l’Artico
L’Italia e l’Antartide
CNR-ISP
National Research Council
Institute of Polar Sciences
c/o Scientific Campus - Ca' Foscari University Venice - Via Torino, 155 - 30172 VENEZIA MESTRE (VE)
Phone: +39 041 2348547 - E-mail: protocollo.isp AT pec.cnr.it
Fax: +39 041 2348 549 - Codice Fiscale: 80054330586 - P.I.:02118311006
Unless otherwise indicated, the content of this site is licensed : Attribution Non Commercial Share Alike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Privacy policy e Cookie policy - Transparent administration (CNR)