Microbial Ecology and Biotechnology LAB (EcoBiM)
 Brief description
Brief description
Experimental activities carried out at the EcoBiM LAB in Messina are addressed to the ecology and biotechnology of microorganisms, particularly prokaryotes, inhabiting both marine and continental polar habitats. The diversity of microorganisms, their response to environmental stress conditions (deriving from natural or anthropogenic forcing, such as climate change and chemical contamination), the astrobiological implications of life in extreme environments, and their evolution and adaptation in polar environments are among the ecological aspects investigated. EcoBiM researchers are also interested in the evaluation of the metabolic capabilities and biotechnological potentialities of cold-adapted microorganisms, by searching for biomolecules exploitable in industrial applications and bacteria able to degrade organic pollutants at low temperatures.
Matrices of interest
The analyzed matrices are mostly attributable to the hydrosphere (marine, river and lake waters, brines) and cryosphere (permafrost, snow, sea-ice and continental ice, intrapermafrost brines), but soils and sediments are also considered. The study of the interactions between microorganisms and biotic (for example, pelagic and benthic organisms) and abiotic (such as microbial communities colonizing polymeric materials, indicated with the term plastisphere) is of particular interest.
Applied experimental approaches
For the microbiological characterization of extreme environments, similarly to the analytical procedures commonly applied for the study of temperate areas, we use both culture-dependent and -independent (i.e. biomolecular and biochemical) approaches, including:
- isolation and maintenance in pure culture of bacterial strains;
- phenotypic (physiological, biochemical and morphological characteristics) and genotypic (analysis of the 16S rRNA sequences and search for functional genes) characterization of cultivable bacteria;
- screening of bacteria for the production for useful biomolecules (including antibiotics, exopolysaccharides, biosurfactants);
- evaluation of the metabolic capacities of the microbial communities through miniaturized assays;
- characterization of the microbial communities by the hybridization in situ with oligonucleotide probes (CARD-FISH);
- extraction of environmental DNA and RNA for metagenomics and metatrascriptomics studies;
- preparation of microcosms enriched with organic and inorganic contaminants, and degradation tests.
Instrumentation
The EcoBiM LAB is equipped with basic instrumentation for environmental and applied microbiology (laminar flow cabinet, autoclave, incubators and thermostated baths, centrifuges, filtration systems, sonicators, spectrophotometers, fluorometers) and molecular biology equipment (thermocycler and equipment for electrophoresis).
For details: Dr. Angelina Lo Giudice - angelina.logiudice AT cnr.it
Biology and Ecosystems
Polar environments are highly biodiverse on a spatial temporal scale as well as at different levels of biological organization, from the molecular level to the entire ecosystem. Recent and rapid climatic and environmental changes give urgency to understanding the response of biological communities to these changes, and their impact in the short and long term. In this context, ISP researchers study the different bio-ecological aspects of the marine and terrestrial ecosystems of both poles. Their research is developed along four main often interconnected research fields.
Biodiversity and adaptation
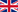
 Polar biological communities are heavily influenced by several local factors concomitant to low temperatures, such as dryness, ice cover, poor nutrient availability, exposure to harmful solar radiation (e.g. UV-B radiation), extremely variable light periods and, in specific cases, high salinities and osmotic stress. Biodiversity guarantees the functioning of all ecosystems, so studying the properties and temporal evolution of polar ecosystem is fundamentally important for improving our knowledge of its current state and predicting its future development, particularly in the light of climate change. The analysis and monitoring of the biodiversity of biological communities and their ecological dynamics constitutes the focal point of this research topic. The study of the morphological-functional adaptation mechanisms adopted by polar organisms for survival in extreme conditions is particularly interesting.
Polar biological communities are heavily influenced by several local factors concomitant to low temperatures, such as dryness, ice cover, poor nutrient availability, exposure to harmful solar radiation (e.g. UV-B radiation), extremely variable light periods and, in specific cases, high salinities and osmotic stress. Biodiversity guarantees the functioning of all ecosystems, so studying the properties and temporal evolution of polar ecosystem is fundamentally important for improving our knowledge of its current state and predicting its future development, particularly in the light of climate change. The analysis and monitoring of the biodiversity of biological communities and their ecological dynamics constitutes the focal point of this research topic. The study of the morphological-functional adaptation mechanisms adopted by polar organisms for survival in extreme conditions is particularly interesting.
Messina
Where we are
The building, in pure Art Nouveau style, is located on the Straits of Messina, in the shadow of the Montorsoli Lantern. Thanks to this position, it dominates the waters of the Straits and the Port. The building consists of a central body with three floors, which houses offices and studios, and two wings, with the laboratories. The ISP building in Messina is shared with the Institute for Biological Resources and Marine Biotechnologies (CNR-IRBIM) and there is also a park of about 10,000 square meters, where there is the main auditorium in a building that was originally the Royal National Shooting range.
How to find us
- By train: if you come from the peninsula, get off at the Villa San Giovanni rail station, then board the BlueJet fast ship heading towards Messina Porto Storico. Otherwise if you come from a Sicilian town, get off at Messina Centrale rail station. Once you arrive in Messina, call our office to arrange transfer by car to the Institute.
- By plane: Catania Fontanarossa is the closest airport. From the airport, take the SAIS-Autolinee bus to Messina Central Station. Once you arrive in Messina, call our office to arrange the transfer by car to the Institute.
- By car: the institute can be reached by car and there is on-site temporary parking available. If you come from the peninsula, once you reach Villa San Giovanni you can board the Caronte ship (runs every 40 minutes) and then, once in Messina, continue by car to the Institute. If, on the other hand, you come from a Sicilian town, take the A18 Messina-Catania, exit at Messina Centro and continue towards the institute following the directions here.
Contact
 ISP Secondary office of Messina
ISP Secondary office of Messina
Responsable
Dr. Maurizio Azzaro
E-mail: responsabile_me AT cnr.it
Spianata S. Raineri 86 - 98122 Messina (ME)
Phone:+39 090 601 5415
Fax: +39 090 669 007
MAP
Special Issue: Contaminants and Microbes in Marine, Lake and River Ecosystems (deadline 31 July 2021 )
 A special issue of Water (ISSN 2073-4441). This special issue belongs to the section Aquatic Systems - Quality and Contamination.
A special issue of Water (ISSN 2073-4441). This special issue belongs to the section Aquatic Systems - Quality and Contamination.
This Special Issue aims to present new research to advance our knowledge on all the aspects related to the proposed subject. Specifically, the topics of interest include but are not restricted to: Emerging and legacy pollutant analyses: occurrence and distribution of selected contaminants in water column and sediment; the role of the microbial community in transferring pollutants to higher trophic levels: to elucidate drivers and followers in this process and identify key-species for contaminant turn-over and accumulation; dynamics of natural microbial communities: to distinguish microbial community structure and function spatial and temporal changes; dynamics of contamination in polar and temperate aquatic ecosystems.
Deadline for manuscript submissions: 31 July 2021
Special Issue Editors: Nicoletta Ademollo (CNR-ISP), Francesca Spataro (CNR-ISP), Jasmin Rauseo (CNR-ISP) and Luisa Patrolecco (CNR-ISP).
Carniel Sandro
 M. Sc. in Environmental Sciences, Ph.D. in Environmental Sciences (oceanography) from the University of Venice. Research Director at the CNR Institute of Polar Sciences, Venice, CNR Researcher since 1997. From 2019 to early 2025, he held the role of Head of the Research Division at NATO STO CMRE in La Spezia.
M. Sc. in Environmental Sciences, Ph.D. in Environmental Sciences (oceanography) from the University of Venice. Research Director at the CNR Institute of Polar Sciences, Venice, CNR Researcher since 1997. From 2019 to early 2025, he held the role of Head of the Research Division at NATO STO CMRE in La Spezia.
He taught classes at the University of Bologna, Ancona, and Bocconi University in Milan, and owns the National Scientific Qualification as Full Professor in the 04/A4 Geophysics sector. Awarded the Office of Naval Research Command Coin, he served as Deputy President of the Ocean Science Division at the EGU (European Geoscience Union) from 2019 to 2024. In 2022, he received the Tridente d’Oro award for scientific and outreach merits and, starting in 2024, was admitted as an International Fellow of The Explorers Club.
He investigates the relationship between oceans and climate with a multi- and interdisciplinary approach. His main area of interest is physical oceanography and the interactions occurring between atmosphere, water and sediments. His research has focused on understanding and numerically modeling the role of currents, winds and waves in the transport of heat and salt in the oceans, and the associated variability in the context of an evolving climate.
The extraordinary role in the redistribution of energy between oceanic and atmospheric masses, and the determination of the related energy transfer along the water column, has been central to his research activities, intertwined with connections to: biogeochemical and sedimentological aspects (transport of nutrients and associated sediments); marine renewable energies; unexploded ordnance in the sea; and risks related to flooding and coastal erosion. He has promoted and developed a series of 3D circulation models coupled with meteorological models, third-generation wave generation and propagation models, and modules for the transport of non-cohesive sediments and biogeochemical modules.
The modeling approach has been validated with data from satellites, remote observations, and in-situ measurements in particularly vulnerable areas in the context of global warming. Along with the use of CTD probes, wave gauges, current meters, and turbidimeters, innovative techniques such as Maritime Unmanned Systems (MUS), seismic oceanography, and turbulence measurements with free-fall profilers have been employed. Author and co-author of over 120 papers in ISI journals with Impact Factor, 2 CNR patents, and 5 popular science books, he is a member of the Editorial Board of Scientific Reports (Nature group), Progress in Oceanography, and Ocean Dynamics.
ResearchGate Google Scholar
Casula Marco
 CTER VI level from November 2014.
CTER VI level from November 2014.
From 2014 to 2018 I worked as a technician at the CNR ISMAR Venice participating in numerous oceanographic campaigns and dealing with reagents, waste disposal, material orders and safety in laboratories. Since 2019 I have been a member of the Institute of Polar Sciences of the CNR, carrying out the following tasks:
- Laboratory technician and use of laboratory instruments;
- Collection, preparation and analysis of samples;
- Maintenance and repair of instruments;
- Preparation and transport of equipment for Arctic missions or mountain trips;
- Logistics Management Laboratories and Reagentaries;
- Instructor for orders on the electronic market;
- Appointment by Computer Protocol;
- Control and Technical Management White Rooms (Clean Rooms).
Staff
Director - PANIERI GIULIANA - direttore.isp AT cnr.it - Phone: +39 041-2348659
Staff
Contact with name.surname AT cnr.it
ADEMOLLO NICOLETTA
- Bologna - Researcher
ANTONELLI GIUSEPPE
- Bologna - Technician
ARGIRIADIS ELENA
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348658
AZZARO FILIPPO
- Messina - Researcher - Phone: +39 090-6015419
AZZARO MAURIZIO
- Messina - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 090-6015415
BARBARO ELENA
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348504
BEATRICI DANIELA
- Roma-Tor Vergata - Technician - Phone: +39 06-45488568
BECHERINI FRANCESCA
- Venezia - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2346761
CAIRNS WARREN RAYMOND LEE
- Venezia - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348992
CARNIEL SANDRO
- Venezia - Research Director
CARUSO GABRIELLA
- Messina - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 090-6015423
CASULA MARCO
- Venezia - Technician (in temporary assignment at another facility of the Institution)
CAVALIERE ALICE
- Bologna - Technologist
CESTER VALENTINA
- Venezia - Technician - Phone: +39 041-2348547
CIALLI PAMELA
- Roma-Tor Vergata - Administrative assistant - Phone: +39 06-45488349
COLUCCI RENATO R.
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 040-3756876
CORAMI FABIANA
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348658
COSENZA ALESSANDRO
- Messina - Technician - Phone: +39 090-6015439
COZZI GIULIO
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348935
CRISAFI FRANCESCA
- Messina - Researcher
DALLO FEDERICO
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348937
DE BIASIO FRANCESCO
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348938
DE BLASI FABRIZIO
- Venezia - Researcher
DECEMBRINI FRANCO
- Messina - Researcher - Phone: +39 090-6015413
DI FRANCO SABINA
- Roma-Montelibretti - Technologist - Phone: +39 06-90672394
DI LEO GUGLIELMO
- Messina - Technician
DI MAURO BIAGIO
- Milano - Researcher - Phone: +39 02-66173404
FILICIOTTO FRANCESCO
- Messina - Researcher - Phone: +39 090-6015420
GABRIELI JACOPO
- Venezia - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348911
GIGLIO FEDERICO
- Bologna - Researcher - Phone: +39 051-6398904
GILARDONI STEFANIA
- Milano - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 02-66173328
GIORDANO PATRIZIA
- Bologna - Researcher - Phone: +39 051-6398902
GREGORIS ELENA
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348937
IAKIMOV MIKHAIL
- Messina - Research Director
LA CONO VIOLETTA
- Messina - Researcher
LA MESA MARIO
- Bologna - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 071-2078838
LA SPADA GINA
- Messina - Researcher
LANGONE LEONARDO
- Bologna - Research Director - Phone: +39 051-6398870
LO GIUDICE ANGELINA
- Messina - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 090-6015414
LUPI ANGELO
- Bologna - Researcher - Phone: +39 051-6399588
MAIMONE GIOVANNA
- Messina - Technician - Phone: +39 090-6015423
MAZZOLA MAURO
- Bologna - Researcher - Phone: +39 051-6399592
MISEROCCHI STEFANO
- Bologna - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 051-6398880
MONTAGNA PAOLO
- Bologna - Research Director - Phone: +39 051-63988913
NOGAROTTO ALESSIO
- Bologna - Technician
PALADINI DE MENDOZA FRANCESCO
- Messina - Researcher
PANSERA MARCO
- Messina - Researcher
PAPALE MARIA
- Messina - Researcher
PATROLECCO LUISA
- Roma-Montelibretti - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 06-90672797
PESCATORE TANITA
- Bologna - Researcher
PLINI PAOLO
- Roma-Montelibretti - Researcher - Phone: +39 06-90672392
PORCINO NUNZIATINA
- Messina - Researcher
RAPPAZZO ALESSANDRO CIRO
- Messina - Technician
RAUSEO JASMIN
- Roma-Montelibretti - Researcher
SACCHETTO ALESSIO
- Padova - Administrative assistant
SALERNO FRANCO
- Milano - Senior Researcher (temporary assignment)
SCALABRIN ELISA
- Venezia - Researcher – Phone: +39 041-2348938
SCIACCA VIRGINIA
- Messina - Researcher
SCLAVO MAURO
- Padova - Research Director - Phone: +39 049 8295907
SMEDILE FRANCESCO
- Messina - Researcher
SPATARO FRANCESCA
- Roma-Montelibretti - Researcher - Phone: +39 06-90672852
SPOLAOR ANDREA
- Venezia - Senior Researcher
TESI TOMMASO
- Bologna - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 051-6398864
TURETTA CLARA
- Venezia - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348947
VALENTINI EMILIANA
- Roma-Montelibretti - Researcher
VARDE' MASSIMILIANO
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348938
VENIER CHIARA
- Venezia - Technologist
VERAZZO GIULIO
- Bologna - Technologist
VITALE VITO
- Bologna - Research Director - Phone: +39 051-6399595
ZANELLA JACOPO
- Padova - Technician - Phone: +39 049-8295714
ZANGRANDO ROBERTA
- Venezia - Senior Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348945
ZANOTTO EMANUELA
- Venezia - Technician - Phone: +39 041-2348902
ZUCCHETTA MATTEO
- Venezia - Researcher - Phone: +39 041-2348937
Other instrumentation available – Headquarters (Venice)

High Performance Liquid Chromatograph Agilent 1100 Series HPLC Systems
Brief description
The HPLC-MS/MS system allows to quantitatively determine polar organic compounds in several environmental and vegetable matrices and biota samples. It is commonly used to investigate specific markers of sources or environmental processes in samples collected in polar regions. It is used to determine levoglucosan, key tracer of biomass burning, in ice core samples to provide historical profiles of fire regimes in paleoclimatic studies. Several water soluble organic compounds (free and combined amino acids, phenolic compounds) are determined using HPLC-MS/MS in aerosol samples to define chemical composition of atmosphere in urban and polar samples. Polar pesticide or toxins are commonly determined with HPLC-MS/MS in fresh water, sea water, biota or vegetable samples.
Instrument
High Performance Liquid Chromatograph Agilent 1100 Series HPLC Systems (Waldbronn, Germany) with a binary pump, vacuum degasser, autosampler and thermostated column compartment coupled with an API 4000 Triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometer (Applied Biosystem/MSD SCIEX, Concord, Ontario, Canada) using a TurboV source.
Contact person: Dr. Roberta Zangrando - roberta.zangrando AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Analysis of discrete samples of several matrices: ice, snow, atmospheric aerosol, lacustrine water, fresh water, sea water, sediment, vegetable and biota samples. Analysis of polar organic compounds such as for example anhydrosugars, amino acids, phenolic compounds, organic acids.
Agilent 1100 series HPLC system coupled with API 4000, High Performance Liquid Chromatograph coupled with tandem mass spectrometer (HPLC-MS/MS). (IMAGE)

Liquid chromatograph UHPLC mod. Dionex Ultimate 3000 Dual Pump RS
Brief description
This instrument is the key system to perform semicontinuous analysis of organic compounds in ice core samples.
Instrument
Liquid chromatograph UHPLC mod. Dionex Ultimate 3000 Dual Pump RS (Thermo ScientificTM) with vacuum degasser, column thermostat.
Contact person: Dr. Elena Barbaro - elena.barbaro AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Semicontinuos analysis of ice cores. This system is coupled with continuous flow analysis (CFA).
Dionex Ultimate 3000 Dual Pump RS Thermo Scientific, Liquid chromatograph UHPLC Dual Pump (IMAGE)

Mercur Plus - Analytik Jena AG, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS).
Brief description
Cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS) is an analytical technique used for the quantification of mercury at trace/ultra-trace levels. This technique is mainly used on “clean” aqueous matrices (eg ice, snow, and water) from remote and uncontaminated areas.
The sensitivity of the instrument is fully harnessed by using official methods such as USEPA1631 version E or UNI-EN 15853: 2010. The Hg present in the matrix is oxidized to Hg2+ with BrCl solution and then reduced to elemental mercury(Hg0) con SnCl2. The Hg0 is stripped from the aqueous matrix using an inert carrier gas (argon) and successively transported to gold traps for the pre-concentration by amalgam formation. Following thermal desorption at T between 450-500 °C, the Hg0 is desorbed from the gold traps and is transported into a quartz cell.
Light from a mercury vapor lamp passes through the quartz cell that contains the sample mercury in a flow of argon carrier gas and excites all the mercury atoms which then emit a characteristic fluorescence radiation at 253.7 nm. The amount of light emitted by the mercury atoms in the sample is proportional to the amount of mercury passing through the quartz cell. The CV-AFS of the CNR-ISP is located inside a dedicated clean room.
Instrument
Mercur Plus - Analytik Jena AG, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS).
Contact person: Dr. Massimiliano Vardè - massimiliano.varde AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Aqueous matrices: atmospheric deposition, snow, ice, drinking water, mineral water, natural water, seawater. Mercury, as total mercury, or as dissolved, filtered and unfiltered after sample pre-treatment.
Mercur Plus - Analytik Jena AG, cold vapor atomic fluorescence spectroscopy (CV-AFS). (IMAGE)

Gas chromatograph coupled with mass spectrometer (GC-MS)
Brief description
The GC-MS system allows the quantification of volatile apolar compounds in environmental matrices. In the environmental field GC-MS finds main application in the determination of persistent organic pollutants (POPs) such as PCBs, PBDEs, PAHs, pesticides, in environmental matrices both in urban and remote areas such as polar areas. As well as it used in the determination of personal care products such as fragrances that have been observed not only in urban areas but also in Antarctica.
In the ISP-CNR there are 3 GC-MS systems. Among these, the system equipped with a cryogenic trap allows the preconcentration of volatile compounds (allowing the quantification of volatile compounds difficult to analyze in GC even at very low levels). There is also a GC-MS system equipped with a pyrolyser that allows the analysis of non-volatile materials such as plastic materials.
Instrument
• GC-MS 7890A-5975C (Agilent) /
• GC-MS GC7890A+MS5975C (Agilent) with cryogenic trap (MARKES Int)
• GC-MS GC6890+MS5973 (Agilent) with Pyrolysis system Pyroprobe 5000 Series
Contact person: Dr. Elena Argiriadis - elena.argiriadis AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice Headquarters
Matrix and type of measurement
Analysis of discrete samples of several matrices: ice, snow, atmospheric aerosol, lacustrine water, fresh water, sea water, sediment, vegetable and biota samples. Compounds analyzed: Apolar volatile compounds such as PCBs, PBDEs, PAHs, pesticids, fragrances, sterols.
GC-MS 7890A-5975C Agilent (IMAGE)
Microplastics and Other Anthropogenic Particles Laboratory (MiP Lab)

Brief description
Microplastics are considered emerging pollutants and they are present in different environmental compartments (e.g. seawater, soil, atmosphere, etc.). In 2019 the European Chemical Agency has clearly defined microplastics and their sizes: “a material composed of solid polymer-containing particles, to which additives or other substances may have been added, with particle dimensions ranging from 1 nm to 5 mm and with fiber lengths ranging from 3 nm to 15 mm and length to diameter ratio of >3. ECHA has also firmly stated the need of polymer identification when analyzing microplastics. Microplastics can be primary and secondary, according to their sources; sources of primary microplastics are discharges from household washing machines, road dust, tire wear and cosmetics. Particles and fibers of plastics can be vector of other pollutants and pathogens. An accurate quantification and characterization of microplastics allow evaluating the environmental risk assessment and designing future actions of environmental management and recovery.
Instrument
Micro-FTIR Nicolet™ iN™10 Infrared Microscope Thermo Scientific, it couples optic microscopy with IR spectroscopy. Two different detectors are present: DTG (Deuturate Triglycine sulfate) detector enables room temperature analysis, and MCT (Mercury Cadmium Telluride ) detector works with liquid nitrogen and allows the analysis of samples down to 10 µm. Samples can be analyzed on transmittance mode, reflectance mode and ATR mode.
Matrix and type of measurement
Non-destructive analysis of microplastics in different environmental samples (seawater, sediments, soil, permafrost, aerosol, snow, raw and treated water, discharges from household washing machines, etc.) and in different biota (crustaceans, mollusks, fish, etc.). Micro-FTIR allows quantification and simultaneous polymer identification of plastic particles and fibers and of additives, plasticizers. and other synthetic and natural fibers. It can be employed for analysis of microplastics, but also for analysis of microfossils, artistic handiworks, etc.
Contact person: Dr. Fabiana Corami - fabiana.corami AT cnr.it - CNR-ISP Venice headquarters
Open Administration
Open administration
The section Open Administration is organized according to Legislative Decree no. 33 of 14 March 2013 Reorganization of the discipline concerning the obligations for advertisement, transparency and diffusion of information by the public administration (GU Serie Generale n. 80, 05/04/2013), as amended by D.lgs. 25 May 2016 n. 97 (GU Serie Generale n. 132, 08/06/2016).
The manager of transparency and bribery prevention of Institute of Polar Sciences is Dr. Giulia Panieri, Director ISP-CNR (email direttore.isp AT cnr.it).
Provision of nomination (no.16 Date: 28/01/2025)
Invitations to tender and contracts
- year 2024
- year 2023
- year 2022
- year 2021
- year 2020
- year 2019
Previous directors:
• Mauro Sclavo - Interim Director (From 1st May 2024 until 31st January 2025)
• Carlo Barbante (From 1st May 2020 until 30th April 2024)
• Leonardo Langone - Interim Director (From 1st June 2019 until 30th April 2020)
 Ministero dell'Universita e Ricerca
Ministero dell'Universita e Ricerca
Programma Ricerche Artico
Programma Nazionale di Ricerca in Antartide
 Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale
Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale
L'Italia e l’Artico
L’Italia e l’Antartide
CNR-ISP
National Research Council
Institute of Polar Sciences
c/o Scientific Campus - Ca' Foscari University Venice - Via Torino, 155 - 30172 VENEZIA MESTRE (VE)
Phone: +39 041 2348547 - E-mail: protocollo.isp AT pec.cnr.it
Fax: +39 041 2348 549 - Codice Fiscale: 80054330586 - P.I.:02118311006
Unless otherwise indicated, the content of this site is licensed : Attribution Non Commercial Share Alike 4.0 International (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0)
Privacy policy e Cookie policy - Transparent administration (CNR)
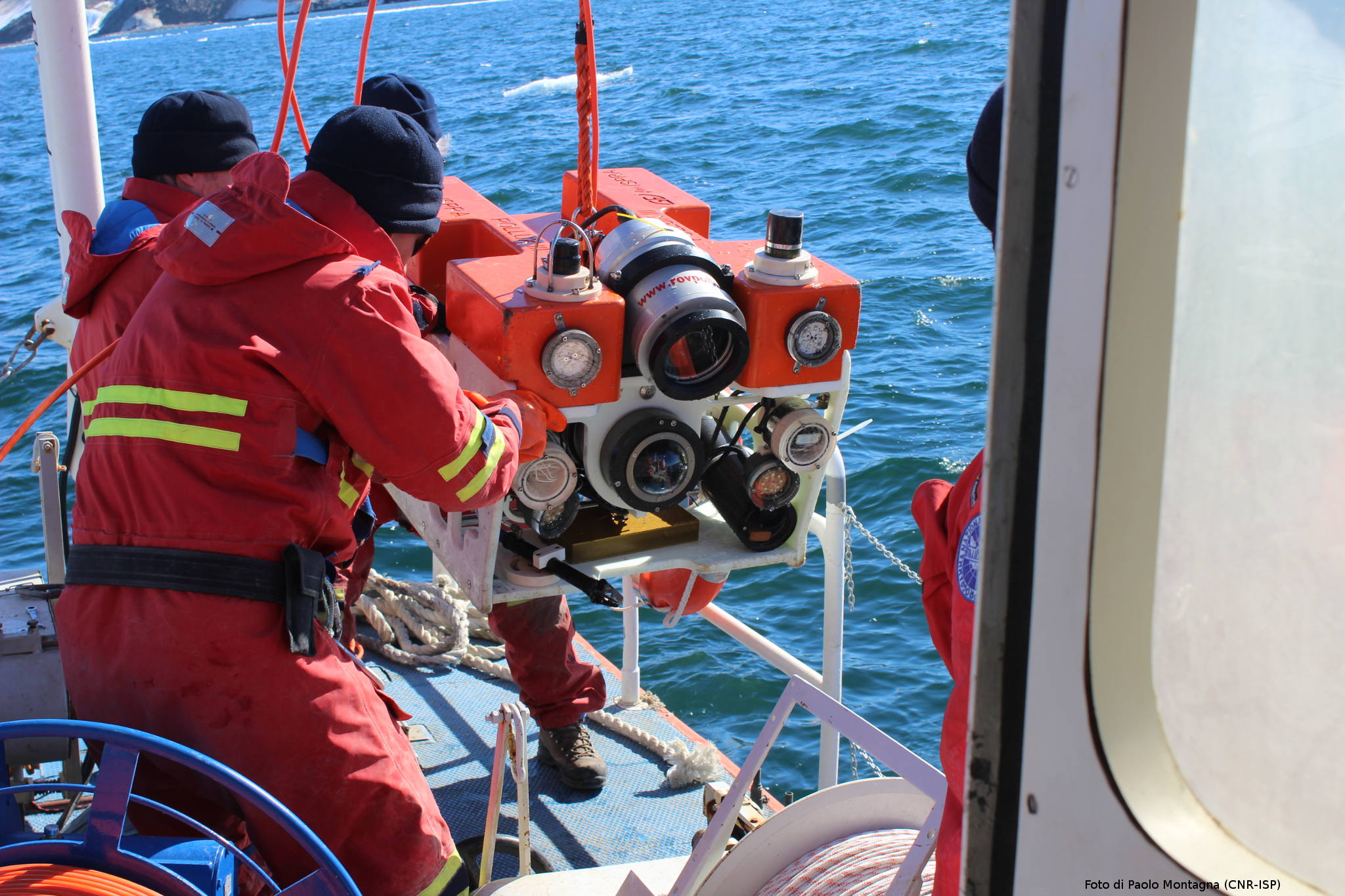
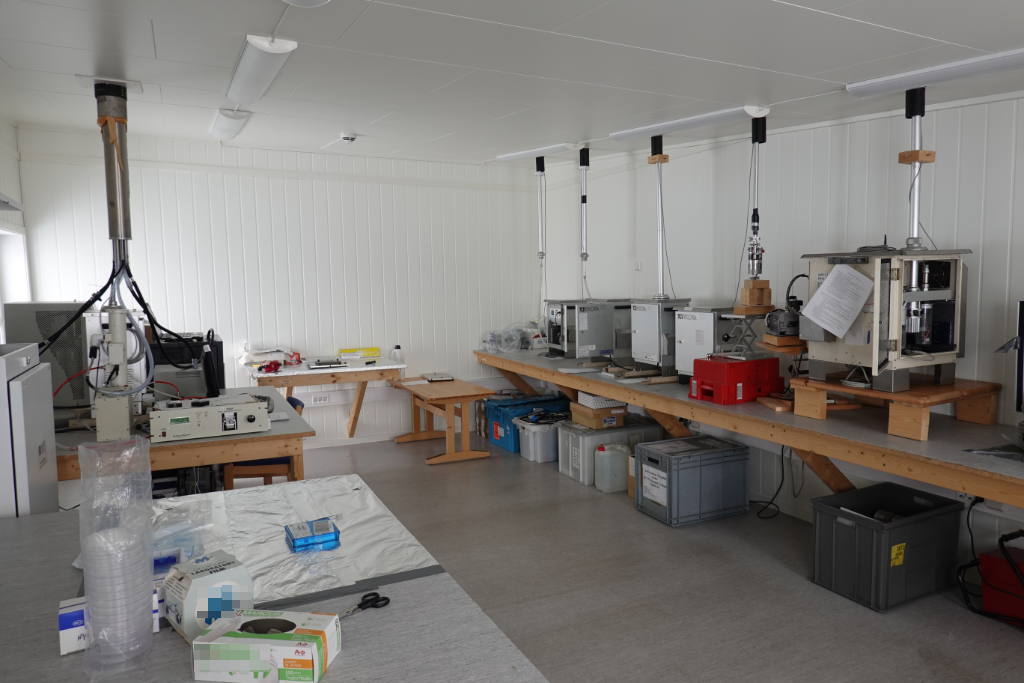
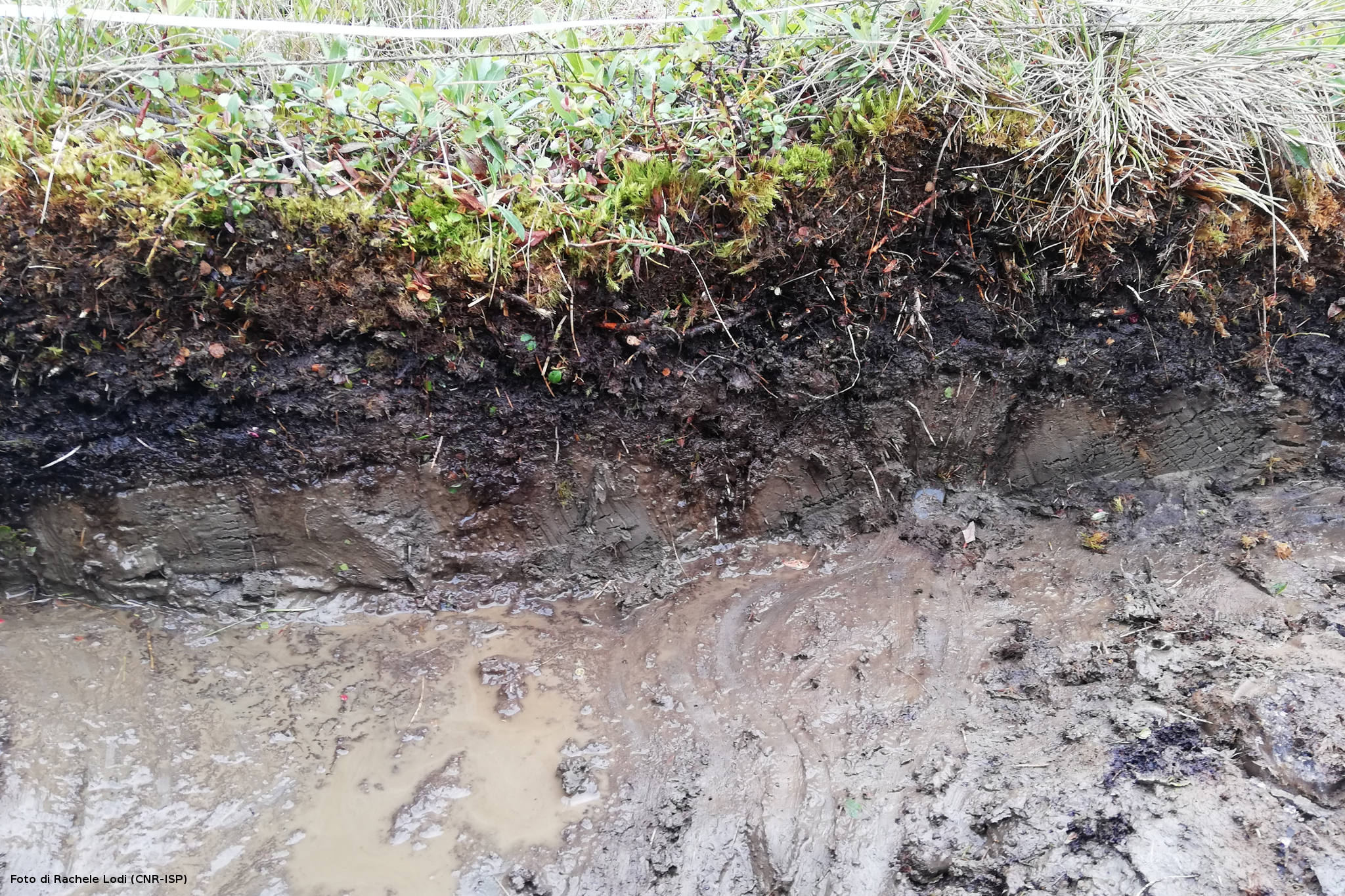
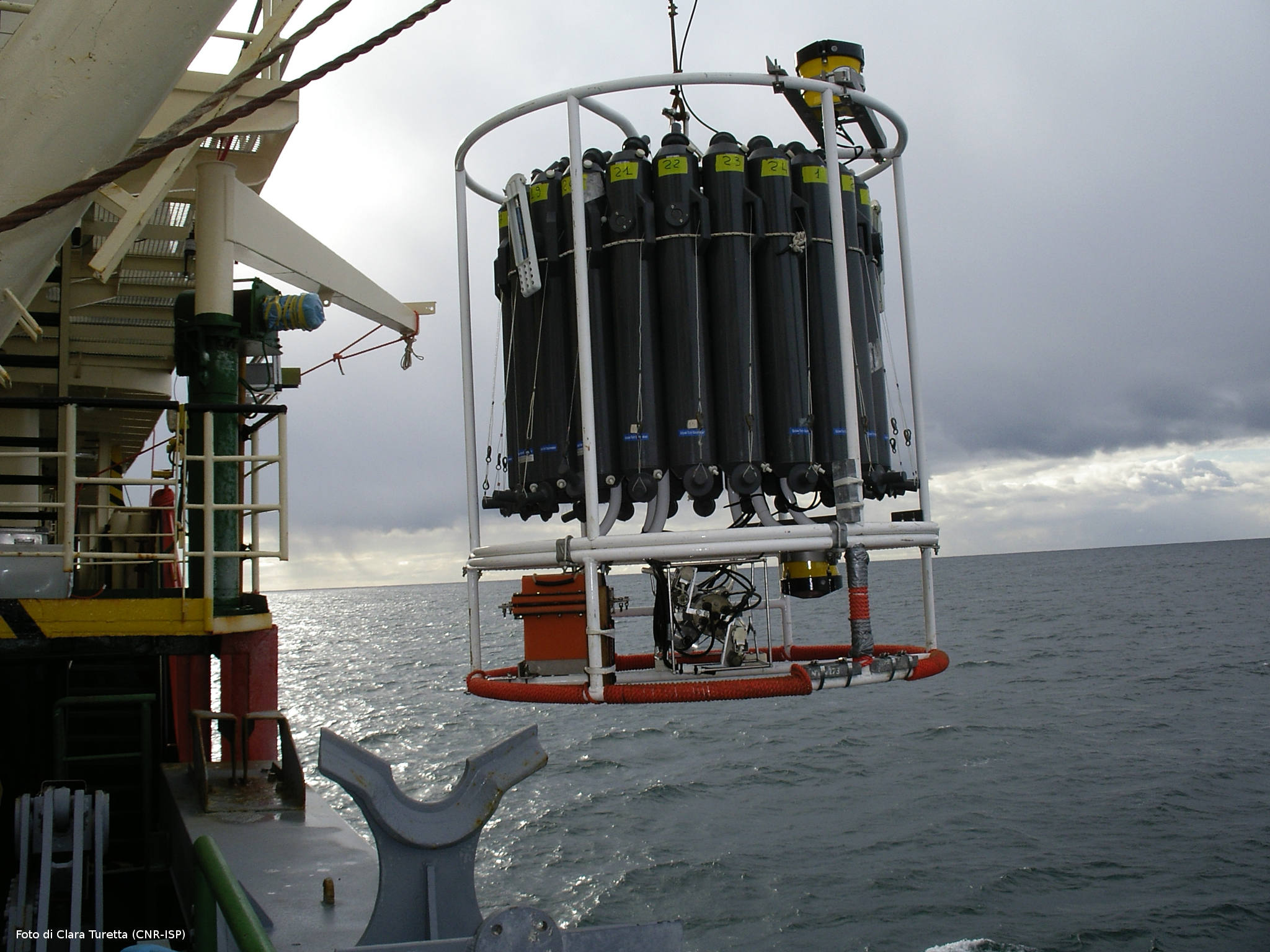
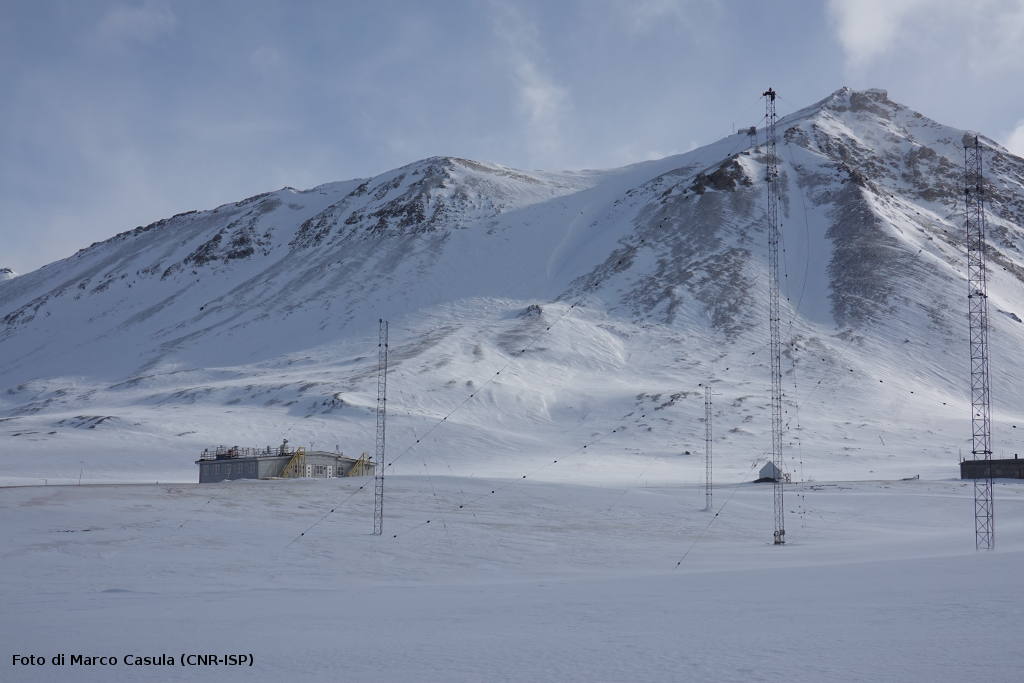
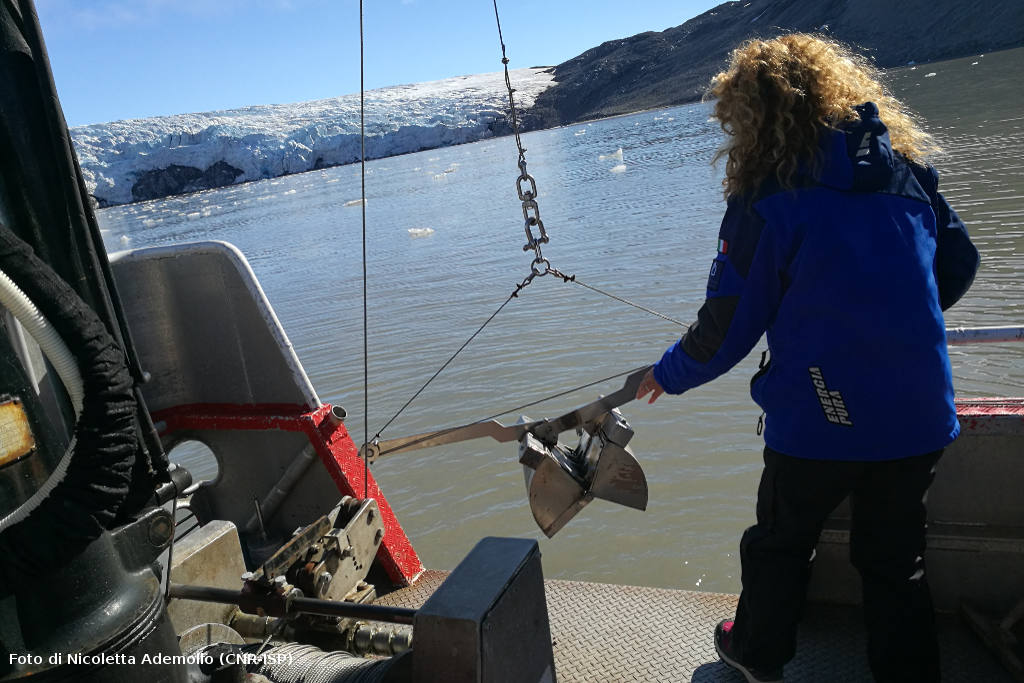
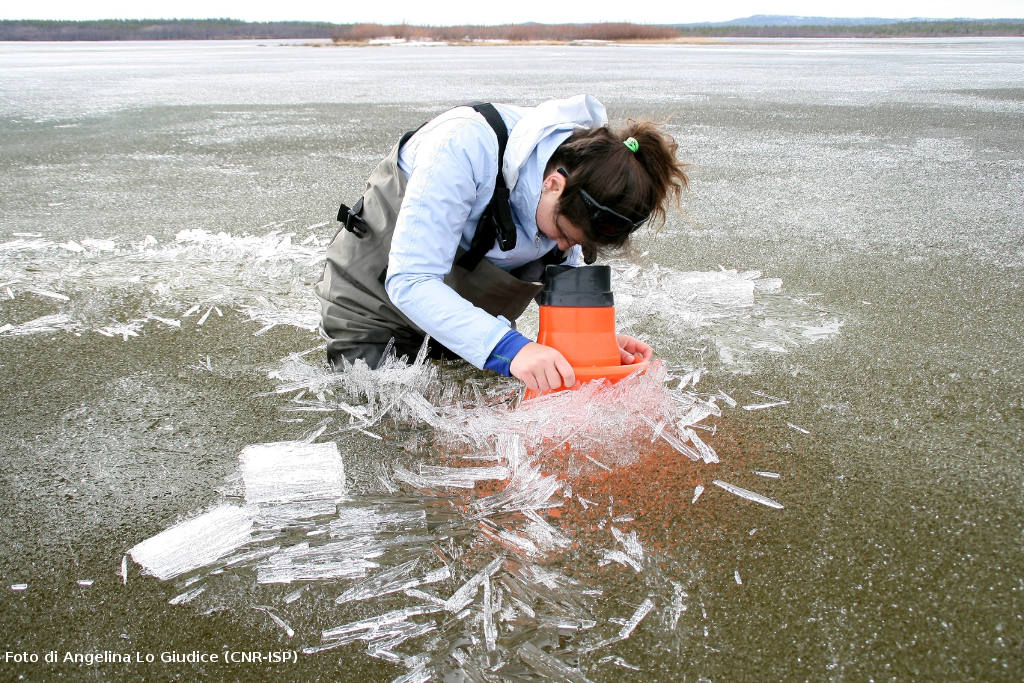
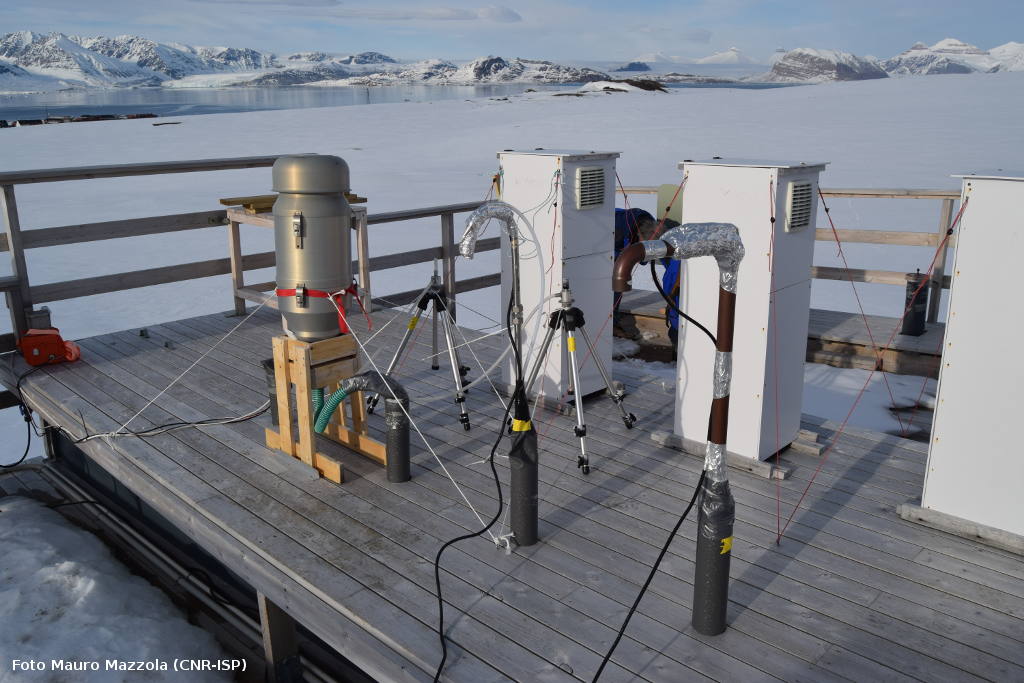
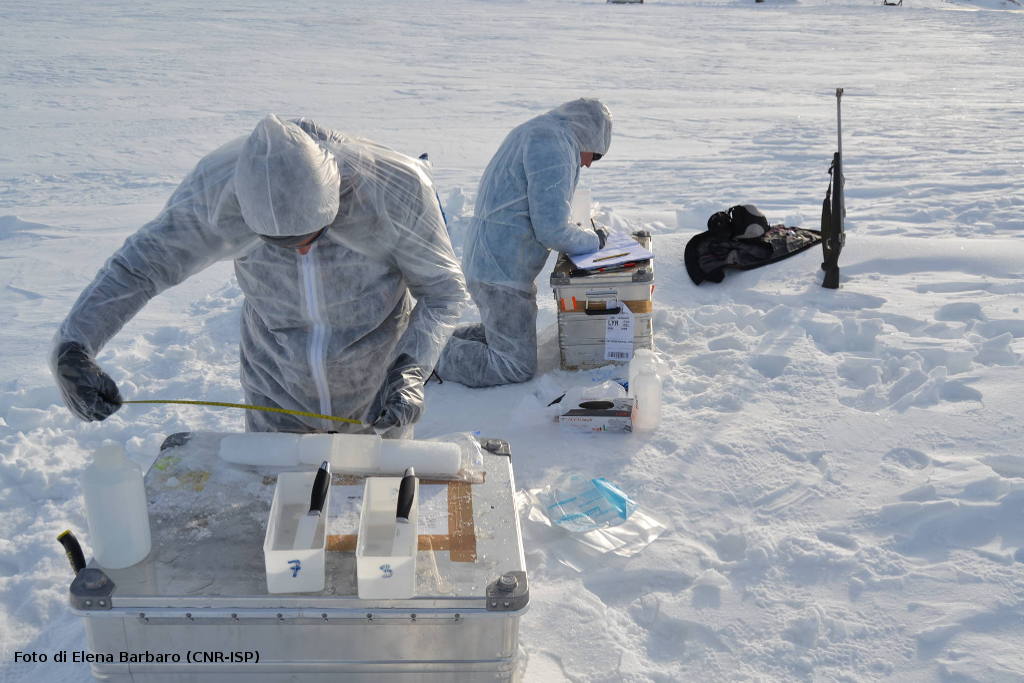






























 Deeper understanding of biological processes and recent advances in biotechnology allow us to use the natural world to progress in various industries, such as in the development of drugs and food additives. In general, the term bioprospecting is used to indicate the exploration of living beings and biological materials for biomolecules that may be useful to humans. In this field, poorly known or poorly described genetic resources have a great potential for the discovery of new and valuable natural products. Therefore, polar organisms, given their unusual metabolic abilities and physiological adaptations to extreme environmental conditions, are well suited for this purpose. Furthermore, the possible future potential of polar organisms in of the bioremediation of pollutants, even persistent ones, at low temperatures should not be overlooked.
Deeper understanding of biological processes and recent advances in biotechnology allow us to use the natural world to progress in various industries, such as in the development of drugs and food additives. In general, the term bioprospecting is used to indicate the exploration of living beings and biological materials for biomolecules that may be useful to humans. In this field, poorly known or poorly described genetic resources have a great potential for the discovery of new and valuable natural products. Therefore, polar organisms, given their unusual metabolic abilities and physiological adaptations to extreme environmental conditions, are well suited for this purpose. Furthermore, the possible future potential of polar organisms in of the bioremediation of pollutants, even persistent ones, at low temperatures should not be overlooked.


