Description of Southern Adriatic Sea Observing Site
The southern Adriatic is the deepest part of the Adriatic Sea with a maximum depth of 1200 m. In its western side, surface waters coming from the northern Adriatic spread southward along the Italian coast, whereas the surface Ionian waters flow along the eastern margin of the basin. Below the surface layer, the MLIW (Modified Levantine Intermediate Water), from the Eastern Mediterranean basin, enters the Adriatic Sea on the eastern side of the Otranto Strait, at 200-600 m depth.
 The southern Adriatic is a site of dense water formation. The Adriatic Deep Water (AdDW) is generated through deep vertical convection, caused by surface heat losses following cold continental wind events occurring in late winter. Occasionally, the North Adriatic Deep Water (NAdDW), produced by surface heat loss and evaporation driven by Bora storms during winter in the Northern Adriatic Sea, contribute to the AdDW. The NAdDW constitutes the densest waters of the whole Easter Mediterranean, it flows mostly along the western shelf of the central Adriatic Sea as a bottom-arrested density current and arrives to the Gargano Peninsula after 2–4 months since it has been produced. Recently shorter arrival times (3-4 weeks) have been observed. Once it reaches the edge of the continental shelf it sinks toward the center of the Southern Adriatic along the slope in front of the Gargano promontory or through the Bari canyon, carrying dissolved oxygen, nutrients, particulate matter, and pollutants to deep benthic ecosystems.
The southern Adriatic is a site of dense water formation. The Adriatic Deep Water (AdDW) is generated through deep vertical convection, caused by surface heat losses following cold continental wind events occurring in late winter. Occasionally, the North Adriatic Deep Water (NAdDW), produced by surface heat loss and evaporation driven by Bora storms during winter in the Northern Adriatic Sea, contribute to the AdDW. The NAdDW constitutes the densest waters of the whole Easter Mediterranean, it flows mostly along the western shelf of the central Adriatic Sea as a bottom-arrested density current and arrives to the Gargano Peninsula after 2–4 months since it has been produced. Recently shorter arrival times (3-4 weeks) have been observed. Once it reaches the edge of the continental shelf it sinks toward the center of the Southern Adriatic along the slope in front of the Gargano promontory or through the Bari canyon, carrying dissolved oxygen, nutrients, particulate matter, and pollutants to deep benthic ecosystems.
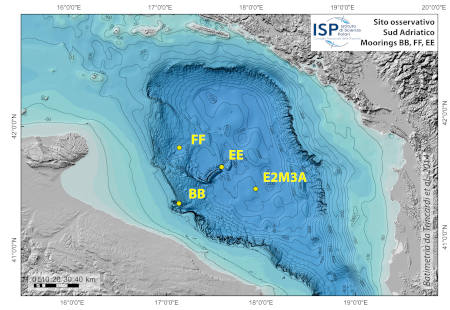
 With the aim to monitor the arrival and the path of the dense waters coming from the northern Adriatic shelf, an observational system has been positioned based on three mooring lines: BB, EE and FF. This observational system has been activated and financed since 2004 by various scientific projects (EU-EuroSTRATAFORM, EU-HERMIONE, PRIN-OBAMA, EU-Perseus, EU-CoCoNet, Italian Flagship Project Ritmare (SP5-WP5-AZ3) and Italian Marine Strategy. In addition, these oceanographic moorings are part of the Italian Fixed Point Observatory Network (IFON) and, are supported by Planning and Grant Office of the CNR.
With the aim to monitor the arrival and the path of the dense waters coming from the northern Adriatic shelf, an observational system has been positioned based on three mooring lines: BB, EE and FF. This observational system has been activated and financed since 2004 by various scientific projects (EU-EuroSTRATAFORM, EU-HERMIONE, PRIN-OBAMA, EU-Perseus, EU-CoCoNet, Italian Flagship Project Ritmare (SP5-WP5-AZ3) and Italian Marine Strategy. In addition, these oceanographic moorings are part of the Italian Fixed Point Observatory Network (IFON) and, are supported by Planning and Grant Office of the CNR.
Since 2021, sites BB and FF, have become part of the European Multidisciplinary Seafloor and water column Observatory European-Research Infrastructure Consortium (EMSO-ERIC) as Regional Facility in the southern Adriatic Sea consisting of moorings BB and FF and observational site E2M3A operated by OGS Trieste. EMSO-ERIC is a European "diffuse" research infrastructure for ocean observation (https://emso.eu/), which enables long-term and also real-time monitoring of ocean processes. It consists of a system of Regional Facilities located at strategic marine sites in the European seas, Northeast Atlantic, Mediterranean Sea and Black Sea. Each site is equipped with multidisciplinary sensors placed on the seafloor and along the water column to continuously measure physical and bio-geochemical parameters that enable understanding and description of marine ecosystems, the monitoring of climate change, and provide information related to natural hazards. Participation in the EMSO-ERIC consortium also includes measurement of vertical fluxes of particulate matter, via of No. 2 sediment traps, in the deep mooring of the E2-M3A observatory (operated by OGS Trieste) located in the center of the Southern Adriatic Pit.
Participation in EMSO-ERIC is also supported by the activities of the consortium's Italian Joint Research Unit (https://www.emsoitalia.it/). Finally, the BB mooring is part of the Network of Long-term Continuous Measurements of Mediterranean Deepwater Temperature and Salinity (CIESM Hydrochanges Program).
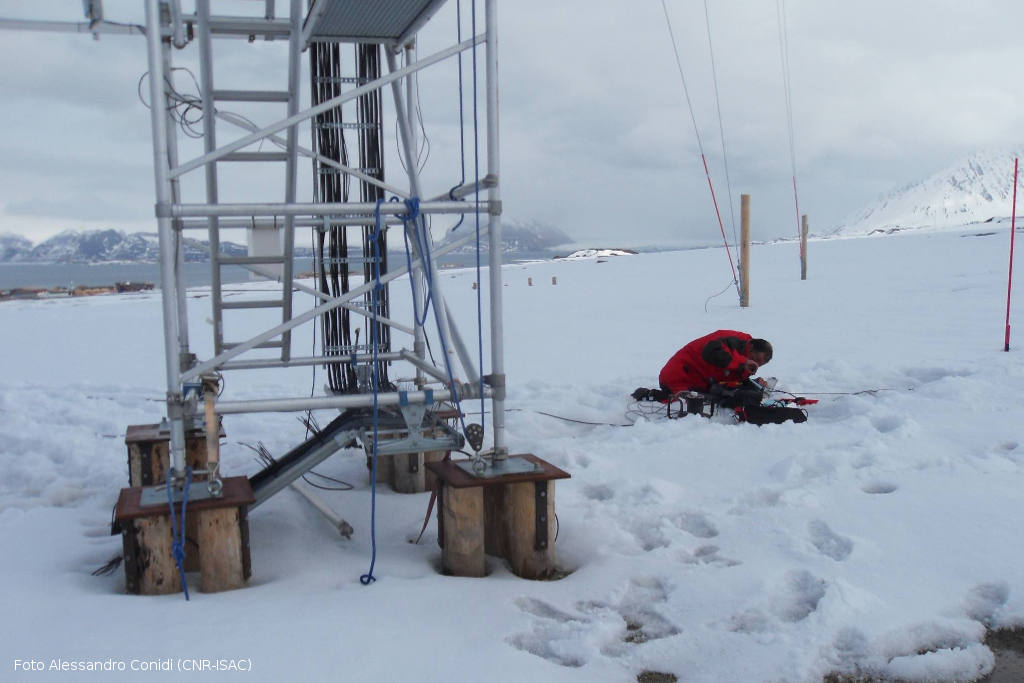
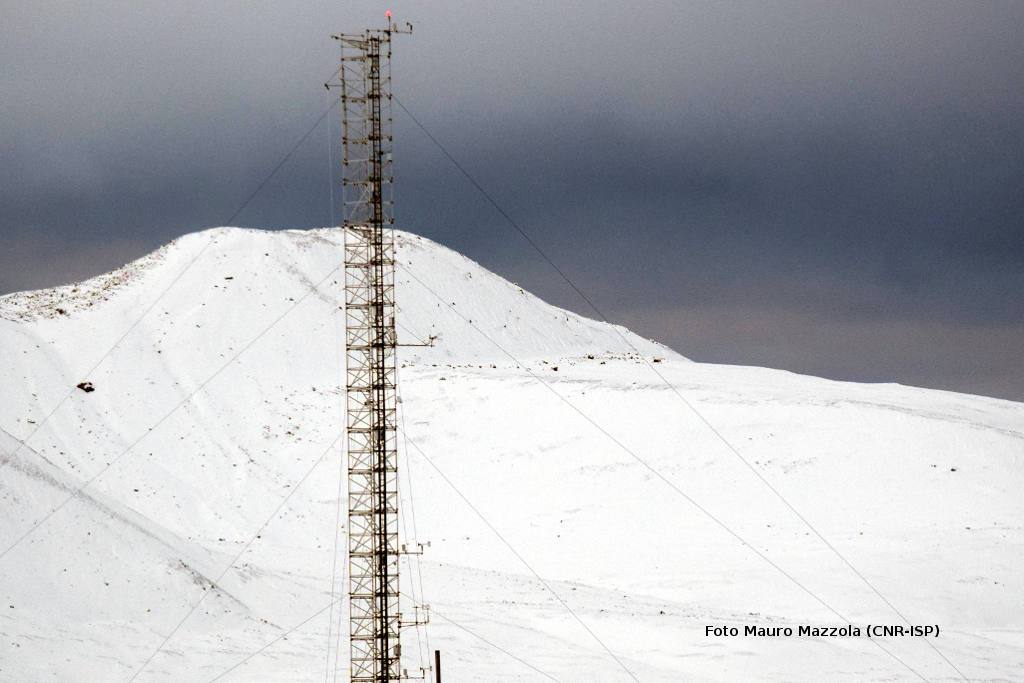
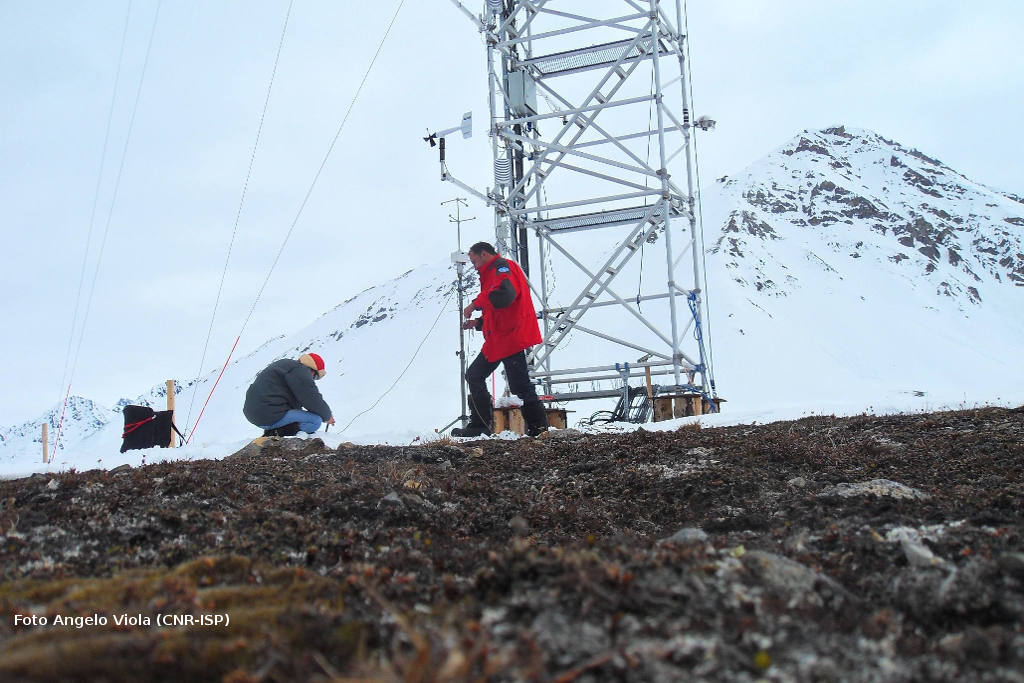
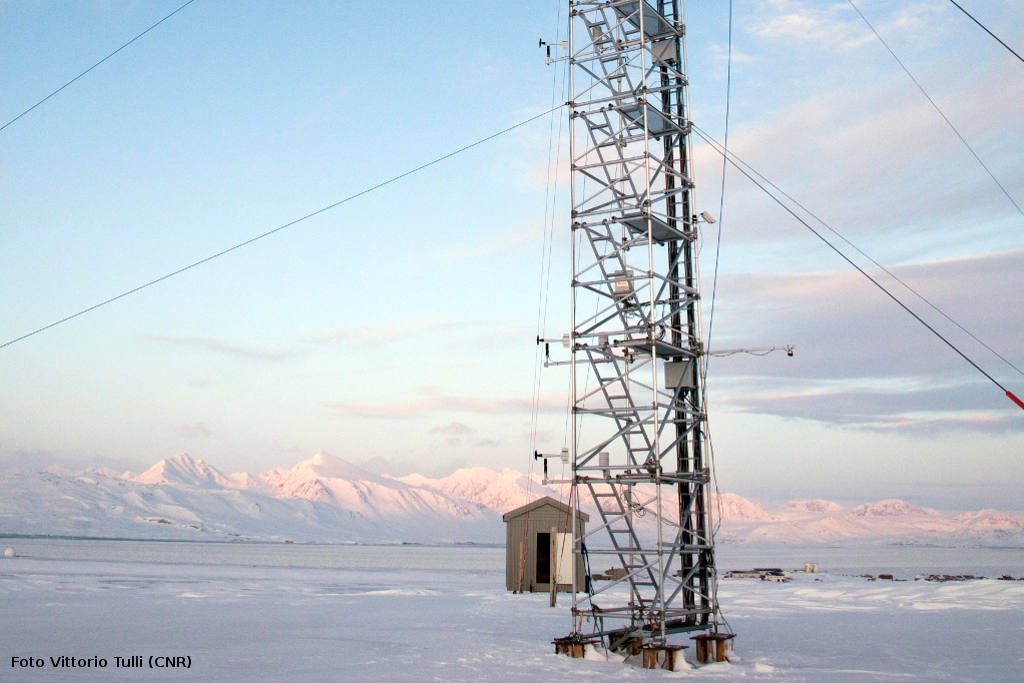
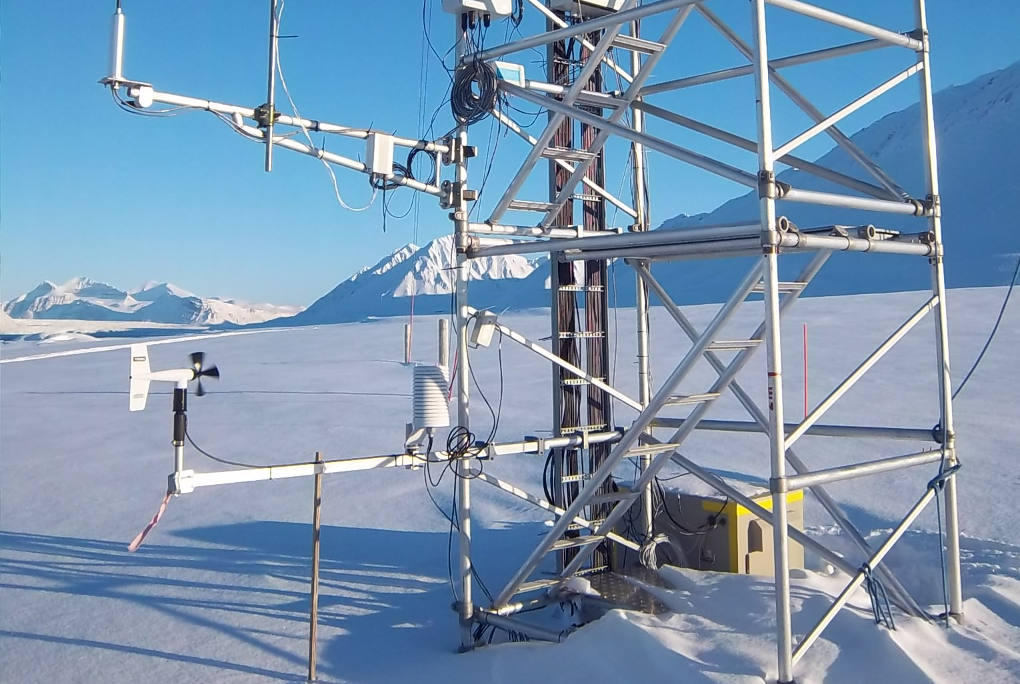
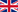
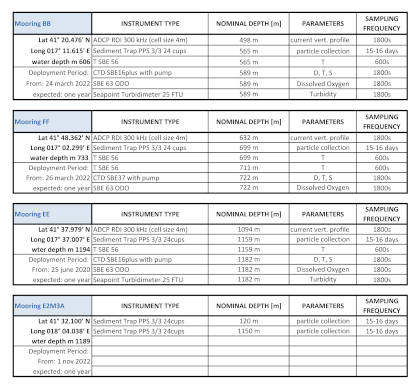
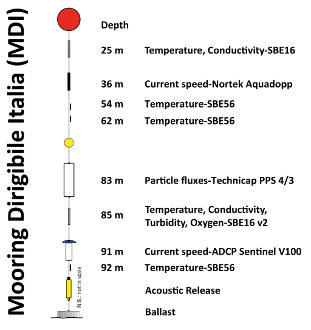
The location of the sites was chosen upon the integration of morpho-bathymetric observations that defined the areas in which the passage of dense waters was more likely with forecasts based on the modeling of the outflow of the North Adriatic dense waters. The BB mooring is located in the northern branch of the Bari canyon, the EE mooring is located in an erosional area west of Dauno seamount, at about 1200m depth, and the FF mooring is on the continental slope in front of the Gargano promontory. Oceanographic sensors are fixed at different heights in the deepest part of the water column (Mooring BB).
The facilities are located offshore and can only be reached by ship. The nearest main docking port is Bari. Site BB is about 20 nm from the port, site FF is about 40 nm, site EE is 45 nm and site E2M3A is about 60 nm.
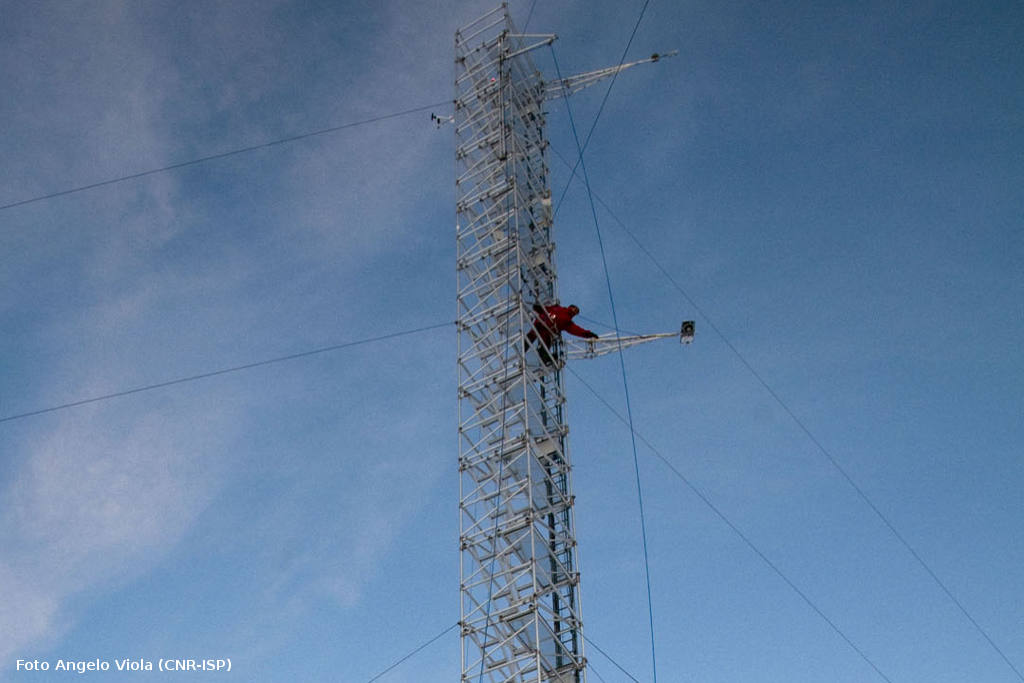
The instruments are equipped with internal memory and power supply. Oceanographic data are downloaded in delayed mode during mooring maintenance, which occurs semi-annually or annually. During maintenance, the moorings are retrieved to perform data offloading, trap sample collection, battery replacement, and functionality verification prior to redeployment. Such servicing have been performed using several CNR research vessels (R/V Urania, R/V Minerva Uno, and N/O G. Dallaporta) or ships of opportunity as part of the experimental activities of the aforementioned projects.
People involved: Stefano Miserocchi (stefano.miserocchi AT cnr.it), Leonardo Langone e Patrizia Giordano.
Main scientific references
Paladini de Mendoza, F., Schroeder, K., Langone, L., Chiggiato, J., Borghini, M., Giordano, P., Verazzo, G., and Miserocchi, S.: Deep-water hydrodynamic observations of two moorings sites on the continental slope of the southern Adriatic Sea (Mediterranean Sea), Earth Syst. Sci. Data, 14, 5617–5635, DOI, 2022.
Paladini de Mendoza Francesco, Katrin Schroeder, Leonardo Langone, Jacopo Chiggiato, Mireno Borghini, Patrizia Giordano, Giulio Verazzo, & Stefano Miserocchi. (2022). Moored current and temperature measurements in the Southern Adriatic Sea at mooring site BB and FF, March 2012-June 2020 (1.1) [Data set]. Zenodo. zenodo.7311090
Miserocchi Stefano, Leonardo Langone, Patrizia Giordano, Vanessa Cardin, Ilaria Conese, Anna Sanchez-Vidal, Giulio Verazzo, & Francesco Paladini de Mendoza. (2022). Biogeochemical data of sinking particulate matter collected by sediment traps at E2M3A mooring (2013-2020) in the Southern Adriatic Sea [Data set]. Zenodo. zenodo.7473396
Paladini de Mendoza, Francesco, Schroeder, Katrin, Langone, Leonardo, Chiggiato, Jacopo, Borghini, Mireno, Giordano, Patrizia, & Miserocchi, Stefano. (2023). Moored echo and turbidity measurements in the Southern Adriatic Sea at mooring site BB and FF, March 2012-June 2020 [Data set]. Zenodo. zenodo.7586134
Paladini de Mendoza Francesco, Katrin Schroeder, Leonardo Langone, Stefano Miserocchi, Mireno Borghini, Patrizia Giordano, Alessandro Amorosi, Jacopo Chiggiato. 2022. Sediment Resuspension and transport processes during dense water cascading events along the continental margin of the southern Adriatic. Submitted to Marine Geology (under revision). Ref.: Ms. No. MARGO-D-22-00290
Langone, L., Conese, I.; Miserocchi, S.; Boldrin, A.; Bonaldo, D.; Carniel, S.; Chiggiato, J.; Turchetto, M.; Borghini, M.; Tesi, T. (2016) Dynamics of particles along the western margin of the Southern Adriatic: Processes involved in transferring particulate matter to the deep basin, Marine Geology,375,28-43. - DOI
Turchetto, M., Boldrin, A., Langone, L., Miserocchi, S. (2012) Physical and biogeochemical processes controlling particle fluxes variability and carbon export in the Southern Adriatic, Continental Shelf Research, 44, 72-82. - DOI
Turchetto M., A. Boldrin, L. Langone, S. Miserocchi, T. Tesi, F. Foglini (2007) Particle transport in the Bari Canyon (southern Adriatic Sea), Marine Geology Volume 246, Issues 2-4, EUROSTRATAFORM: Role and functioning of Canyons, Pages 231-247. - DOI