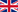
Arctic: The “Sir David Attenborough” Icebreaker Begins its Oceanographic Expedition to Greenland (British Antarctic Survey) to Study Glacier Melting
It started on July 19, 2024, the first six-week scientific expedition to Greenland by the Royal Research Ship (RRS) David Attenborough from the British Antarctic Survey (BAS). This mission is part of the Kang-Glac - Assessing ocean-forced, marine-terminating glacier change in Greenland during climatic warm periods and its impact on marine productivity project, led by an interdisciplinary team of 40 scientists and support staff from research institutes worldwide, including our ISP researchers. The team will focus on key sites near Kangerlussuaq Fjord, aiming to quantify the rates of ice loss from major glaciers and assess the life in the coastal waters of southeastern Greenland, one of the areas on the planet most affected by climate change, while evaluating the impacts on ocean circulation and marine productivity. The ship, one of the most advanced polar research vessels in the world, will operate in southeastern Greenland to enhance understanding of the rapid decline of the region’s ice sheet and its impacts on the climate.
Artico: al via la spedizione oceanografica in Groenlandia della rompighiaccio “Sir David Attenborough” (British Antarctic Survey) per studiare la fusione dei ghiacciai
E' partita il 19 luglio 2024, la prima spedizione scientifica di sei settimane in Groenlandia della nave oceanografica rompighiaccio Royal Research Ship (RRS) Sir David Attenborough del British Antarctic Survey (BAS). La missione fa parte del progetto Kang-Glac - Assessing ocean-forced, marine-terminating glacier change in Greenland during climatic warm periods and its impact on marine productivity, guidata da un team interdisciplinare di 40 scienziati e personale di supporto provenienti da istituti di ricerca di tutto il mondo tra cui le nostre ricercatrici ISP. Il team si concentrerà su siti chiave vicino al fiordo di Kangerlussuaq, con l'obiettivo di quantificare i tassi di fusione dei principali ghiacciai e la vita nelle acque costiere della Groenlandia sud-orientale, una delle aree del Pianeta più colpite dal cambiamento climatico, valutando gli impatti sulla circolazione oceanica e sulla produttività marina. La nave, una delle più avanzate al mondo per la ricerca polare, lavorerà nella Groenlandia sudorientale per approfondire la comprensione della rapida diminuzione della calotta glaciale della regione e dei suoi impatti sul clima. (Chiusura della campagna)
(English version)
Luisa Patrolecco (CNR-ISP), Nicoletta Calace (ISPRA).
 Ministero dell'Universita e Ricerca
Ministero dell'Universita e Ricerca
Programma Ricerche Artico
Programma Nazionale di Ricerca in Antartide
 Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale
Ministero degli Affari Esteri e della Cooperazione Internazionale
L'Italia e l’Artico
L’Italia e l’Antartide
CNR-ISP
Consiglio Nazionale delle Ricerche
Istituto di Scienze Polari
c/o Campus Scientifico - Università Ca' Foscari Venezia - Via Torino, 155 - 30172 VENEZIA MESTRE (VE)
Salvo diversa indicazione, il contenuto di questo sito è concesso in licenza : Attribuzione - Non commerciale - Condividi allo stesso modo 4.0 Internazionale (CC BY-NC-SA 4.0) 
Privacy policy e Cookie policy - Amministrazione trasparente CNR